Since the iPhone X was introduced with the 3D sensing module, its core component VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitter Laser) has been placed under the spotlight of the high-tech stage. Apple‘s strong support has made VCSEL a dazzling star in the technology world. Although VC laser is not a new technology, its birth dates back to the 1980s and commercialized as early as 1996.
Analysis of infrared laser and VCSEL technology
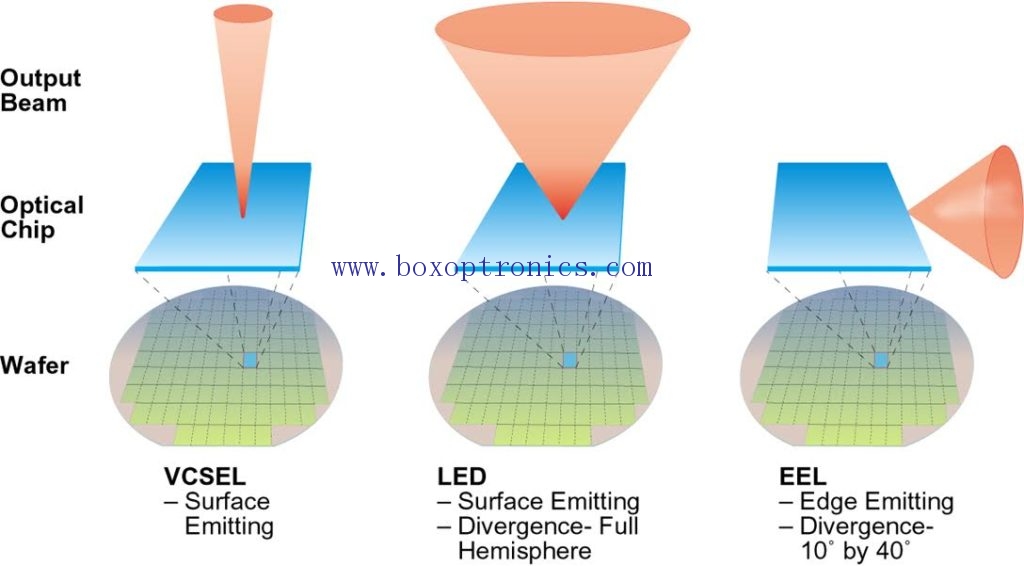
Compared with infrared light-emitting diodes, infrared lasers have the advantages of resonant cavity design, small light divergence angle, high light energy conversion efficiency, and fast data transmission. Because the product design uses pulsed light, it is harmless to the eyes. As technology advances, infrared lasers have increasingly been used in sensing components, and their applications have expanded from industrial applications to commercial and consumer markets.
The infrared laser includes two kinds of VCSEL and EEL (edge emitting laser), and the former has the advantages of small threshold current, circular symmetry of the outgoing beam, high light energy conversion efficiency, high uniformity of the light source and high directivity.
VCSEL "treasure" to be digging in consumer electronics and automotive electronics applications
In recent years, VCSELs have become more and more widely used in the consumer market, including distance sensing, autofocus, 3D sensing (structured light and time of flight), iris recognition, air and water quality testing. Among them, 3D sensing applications include residential automation, robotics, computers, games, virtual fitting rooms, televisions, automobiles, biometrics and wearables.
In addition, VCSEL can also remove speckle, has a symmetrical circular beam, easy to control the illumination angle through the lens, and can provide high-resolution images for automotive night vision illumination, which has broad application prospects.
The key to the success of the 3D sensing market: algorithm and supply chain collaboration
The VCSEL supply chain has been formed. The upstream epitaxial wafer and chip suppliers include IQE (UK), Yulu (II-VI, USA), Epistar (Taistar), Hualijie (HLJ, Taiwan), and stable (Win Semi, Taiwan) and Hongjieke (AWSC, Taiwan), infrared laser suppliers including Finisar (USA), Lumentum (USA), NeoPhotonics (USA), Princeton Optronic (USA), PhilipsPhontonics (Netherlands) and OSRAM OS ,Germany).
Despite the surge in demand for VCSELs after the introduction of the iPhone X, due to the high sensitivity of infrared laser products to temperature, high temperature rises can cause large-scale light attenuation, and VCSEL technology is very demanding on reliability. Product life and quality reliability are the main obstacles to improving yield, and are the main reason for the current shortage of VCSELs for mobile phones.
After Apple, other major mobile phone brands have begun to work with downstream suppliers to try to build a complete supply chain, but they face patent barriers to algorithms. With the development of algorithmic third-party applications and the improved price/performance of 3D sensing modules, 2018 is a crucial year for the deployment and development of VCSEL.