Semiconductor materials form a concentration gradient of charged particles by injecting current, forming a PN junction between two regions with different concentrations of charged particles. When an external current passes through the PN junction, electrons and holes will recombine in the PN junction, emitting photons, forming a laser.
The packaging technology of semiconductor lasers is an important link to ensure their normal operation and improve reliability. Common packaging technologies include TO (metal shell), COB (chip bonding), DIP (dual inline packaging), SMD (surface mount packaging), and so on. The selection of packaging technology should be determined based on the application and requirements of the laser.
Semiconductor lasers are an important optoelectronic device with broad application prospects. Through continuous research and innovation, the performance and reliability of semiconductor lasers have been significantly improved, and will continue to promote the development of communication, medical, material processing and other fields. In the future, with further technological breakthroughs, semiconductor lasers are expected to achieve commercialization in more application scenarios, bringing more convenience and innovation to human society.
Classification of semiconductor lasers
1. Laser diode (LD), also known as injection laser diode (ILD), is the most common semiconductor laser with advantages such as high efficiency, small size, and low cost.
2. Vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL): The laser beam of VCSEL is emitted perpendicular to the chip surface, suitable for high-speed communication and fiber optic sensing applications.
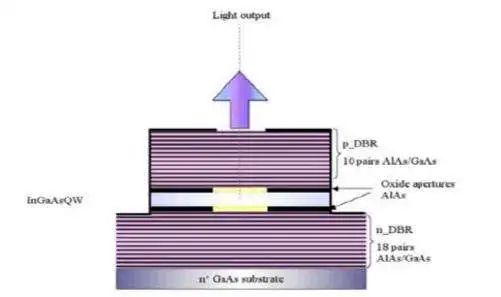
3. Hybrid structure laser: Utilizing the advantages of different materials and combining multiple structures to achieve specific performance requirements.
4. External cavity laser diode (ECL): An external cavity is added to the output end of the laser diode to improve the power and spectral characteristics of the laser.
5. Quantum well lasers: Introducing quantum well structures into semiconductor materials to improve the performance and reliability of lasers.

